1437 Check If All 1's Are at Least Length K Places Away
Given an array nums of 0s and 1s and an integer k, return True if all 1's are at least k places away from each other, otherwise return False.
Example 1:
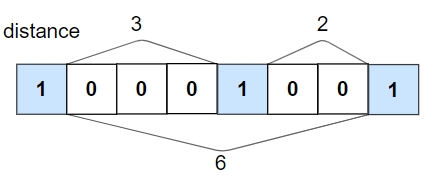
Input: nums = [1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1], k = 2
Output: true
Explanation: Each of the 1s are at least 2 places away from each other.Example 2:
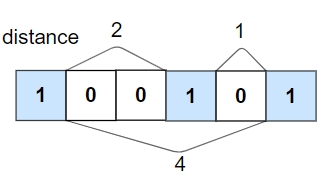
Input: nums = [1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 2
Output: false
Explanation: The second 1 and third 1 are only one apart from each other.Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1], k = 0
Output: trueExample 4:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,1], k = 1
Output: trueConstraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1050 <= k <= nums.lengthnums[i]is0or1
一开始想到的是strstr那样的解法,还是调了一阵子才不off by one。T: O(n)
public boolean kLengthApart(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k < 0) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == 0) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < k && j + i + 1 < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i + j + 1] == 1) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}一看答案,发现自己傻了
public boolean kLengthApart(int[] nums, int k) {
// initialize the counter of zeros to k
// to pass the first 1 in nums
int count = k;
for (int num : nums) {
// if the current integer is 1
if (num == 1) {
// check that number of zeros in-between 1s
// is greater than or equal to k
if (count < k) {
return false;
}
// reinitialize counter
count = 0;
// if the current integer is 0
} else {
// increase the counter
++count;
}
}
return true;
}这题的一个变种是给你一个integer,让你判断它的二进制representation是否符合这个规则。那个得用bit manipulation来做,听说是前东家的题。这里把nums变integer来做模拟。
这个做法主要是从屁股开始,一边remove 0一边数数,数到有1的话,我们check一下是不是起码有k个,如果小于k的话,就return false。
public boolean kLengthApart(int[] nums, int k) {
// convert binary array into int
int x = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
x = (x << 1) | num;
}
// base case
if (x == 0 || k == 0) {
return true;
}
// remove trailing zeros
while ((x & 1) == 0) {
x = x >> 1;
}
while (x != 1) {
// remove trailing 1-bit
x = x >> 1;
// count trailing zeros
int count = 0;
while ((x & 1) == 0) {
x = x >> 1;
++count;
}
// number of zeros in-between 1-bits
// should be greater than or equal to k
if (count < k) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}Last updated
Was this helpful?